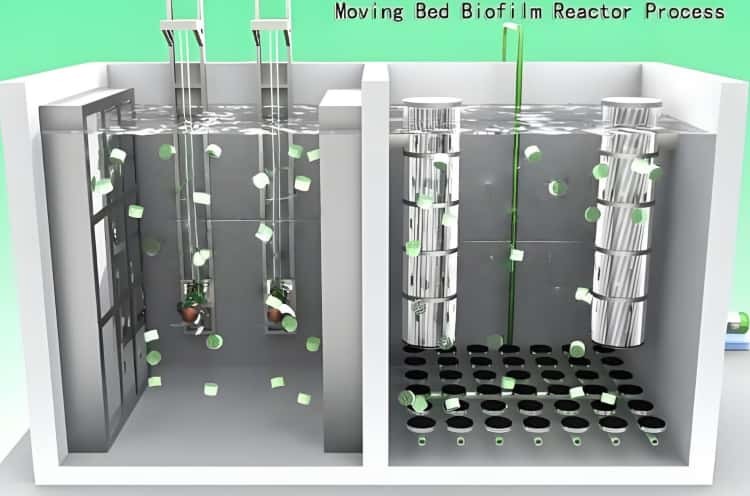
The Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) is an advanced biological wastewater treatment technology that combines the benefits of the conventional activated sludge process and fixed-film systems. The heart of the MBBR treatment system is the specially designed floating biofilm carriers, also known as mbbr media. These carriers provide a large protected surface area for microorganisms to attach and grow, enabling highly efficient pollutant removal within a compact footprint.
Developed in Norway in the late 1980s, MBBR wastewater treatment technology has gained global recognition for its efficiency, flexibility, and robustness. It is now widely used in municipal, industrial, and aquaculture wastewater treatment applications.
What is MBBR Media?
MBBR media, also referred to as biofilm carriers or biological filter elements, are lightweight plastic components with unique shapes designed to maximize surface area for microbial attachment. Suspended within aeration or anoxic tanks, they remain in constant motion through aeration or mechanical mixing, ensuring uniform treatment and biofilm growth.
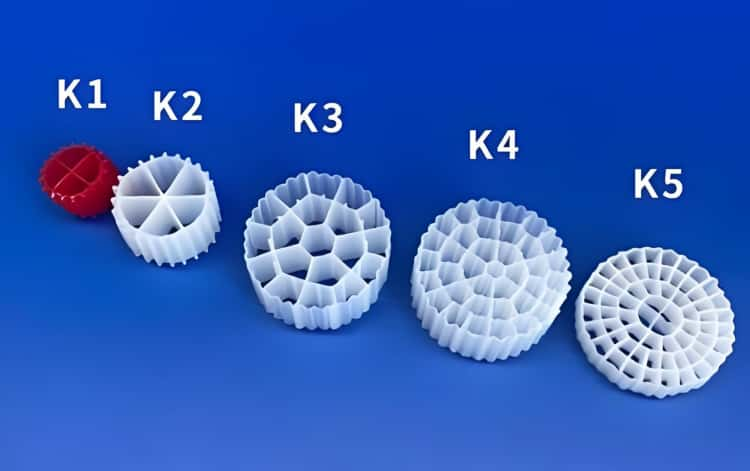

Key characteristics of MBBR media include:
- Material: Commonly made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP), ensuring resistance to wear, corrosion, and biodegradation.
- Shape and design: Typically cylindrical, wheel-shaped, or porous, with internal fins or partitions to maximize protected surface area and prevent clumping.
- Specific surface area: Ranges between 300–1,000 m²/m³, supporting high biomass concentration without increasing tank volume.
- Density: Slightly lower than water (0.94–0.96 g/cm³), allowing the carriers to remain suspended.
- Size: Usually 10–25 mm in diameter, balancing hydraulic flow and biofilm attachment.
- Filling ratio: Occupies 30–70% of reactor volume, depending on treatment objectives.
- Environmental compliance: Non-toxic, recyclable, and often certified for safe use (e.g., NSF/ANSI for potable water applications).
How the MBBR Process Works
The moving bed biofilm reactor process relies on biofilm growth on the media surface to degrade organic matter and nutrients. Its operation includes several steps:
- Influent introduction: Wastewater enters the reactor and mixes with suspended carriers.
- Biofilm development: Microorganisms attach to the carrier surface, forming biofilms of 0.1–2 mm thickness.
- The outer aerobic layer removes BOD/COD and supports nitrification.
- The inner anoxic layer enables denitrification.
- Aeration and mixing: Blowers or mixers keep carriers in motion, ensuring oxygen and pollutant transfer while naturally controlling biofilm thickness.
- Pollutant degradation:
- Heterotrophic bacteria degrade organics (BOD/COD).
- Nitrifying bacteria oxidize ammonia to nitrate.
- Denitrifiers convert nitrate into nitrogen gas.
- Effluent separation: Outlet screens or sieves retain carriers within the reactor while discharging treated effluent.
- Optional recirculation: In advanced systems, effluent recirculation enhances nutrient removal.
MBBR systems can be configured as single-stage (focused on BOD removal) or multi-stage (for nutrient removal). In some cases, they are integrated with activated sludge to form IFAS systems (Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge).

Advantages of MBBR Wastewater Treatment Media
- High efficiency: Achieves 90–95% BOD removal and effective nutrient reduction.
- Stable operation: Biofilm diversity increases process resilience against load fluctuations.
- Compact footprint: Requires less space than conventional systems.
- Low sludge production: Generates less excess sludge than suspended-growth processes.
- Shock load resistance: Biofilm carriers buffer against sudden hydraulic or pollutant surges.
- Durability and cost-effectiveness: Media lifespan can reach 10–20 years, reducing long-term costs compared to other advanced systems.
Applications of MBBR Treatment
MBBR technology is versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Municipal wastewater treatment plants: Secondary treatment for BOD and nutrient removal.
- Industrial wastewater treatment: Effective for food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, pulp and paper, textiles, chemicals, and metal finishing.
- Aquaculture and fish farming: Removes ammonia and organic waste in recirculating systems.
- Decentralized wastewater treatment: Compact packaged plants for remote communities, resorts, or small industries.
- Plant upgrades: Enhances overloaded activated sludge facilities by increasing treatment capacity.
Design and Selection Considerations
When designing an MBBR system, several factors must be taken into account:
- Media selection: Match surface area and structure to wastewater characteristics and treatment goals.
- Reactor design: Based on organic loading rate (1–5 kg BOD/m³·d) and hydraulic retention time (1–4 hours).
- Aeration requirements: Maintain dissolved oxygen at 2–4 mg/L in aerobic zones.
- Carrier retention: Screens or sieves smaller than media size prevent carrier washout.
- Monitoring: Key parameters include biofilm thickness, sludge volume index (SVI), and effluent quality.
Operation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
- Routine inspections: Check for carrier wear, screen blockages, and biofilm growth.
- Cleaning: If excessive fouling occurs, carriers can be periodically removed and washed.
- Common issues and solutions:
- Carrier loss: Replace or repair damaged outlet screens.
- Uneven distribution: Adjust aeration or mixing.
- Foaming: Control with antifoam agents or adjust solids retention time.
With proper design and maintenance, carriers typically last 10–15 years before replacement is required.
Conclusion
MBBR wastewater treatment media is a core component of the moving bed biofilm reactor process, offering an efficient, reliable, and sustainable solution for modern wastewater challenges. By providing an ideal environment for biofilm growth, MBBR systems deliver high treatment performance within a small footprint.
Whether for municipal upgrades, industrial treatment, or decentralized systems, MBBR treatment technology ensures compliance with strict discharge standards while minimizing costs and environmental impact. For project-specific applications, consulting with engineering experts or MBBR media suppliers is recommended to achieve the best results.